Tutorial: Step by step on how to brainstorm

Conteúdo
Do you know how to brainstorm? This is an old technique, but brainstorming is still widely used for one simple reason: it works!
In this post, you will find out how to run a brainstorming session and how it works. Let’s go?
How to brainstorm, step by step
Before going on to explain the brainstorming process steps, let’s better understand this methodology?
What is Brainstorming?
Brainstorming refers to a technique of letting thoughts flow without judgment within a team. This technique was created in 1942 and can be used in various environments and situations, with the aim of creating new ways of seeing problems, have marketing ideas, defining causes and their possible solutions, as well as exploring the creativity of the participants for the emergence of new ideas.
Contrary to popular belief, brainstorming should not be conducted as a chat, in which ideas can simply “fall from the sky.”
It is important to have a conducive environment for participant input to take place, and is best executed when there is a coordinator-mediated roadmap and the process is split into steps.
Thus, a well-built Brainstorm is a useful technique in adding knowledge to participants and assisting in problem management.
Brainstorming enters the Planning phase of the PDCA methodology, focused on the Process Analysis and Action Plan, as it can determine the causes that act on the problem and counteract these issues by creating plans of action.
The PDCA Planning phase also encompasses Goal Setting / Problem Identification and Phenomenon Analysis, which do not fit the use of Brainstorming because they focus on further analysis of the problem / goal and its own identification.
How to run a brainstorming session
Now, you will see how to brainstorm step by step.
For a successful brainstorming meeting, there needs to be a facilitator to manage the four steps of the technique.
They should be a person with experience on the subject matter and should focus on the detailed explanation of each step, ensuring that they are clear to the contributors, so that there is no hastiness or disorder.
The facilitator must also ensure that the environment is adequate so that no contribution is ridiculed, valuing the freedom of expression and participation of employees.
Their role is to be a facilitator and creator of a comfortable environment for everyone.
Brainstorming can be done by dividing it into 4 steps.
It is interesting not to prolong them too much, at least 50 minutes long so that the process does not become tiresome and difficult to pay attention to. If it is not possible to shorten the meetings, it is advisable to divide the development of the steps into more meetings if necessary.
Using the step script proposed here is not mandatory, but it is an interesting tip to ensure greater success in engaging people and understanding and solving problems. Let’s see how to brainstorm step by step:
Step 1: Explanation of the Goal / Problem
The facilitator explains to the group what is the goal or problem to be analyzed. All available information about the object of study should be given to the collaborators so that the preparation for Brainstorming is done as completely and didactically as possible. That done, it is advisable to give some initial thought to the factors that influence the problem, and to think about the various perspectives that involve both the cause of the problem and its solution.
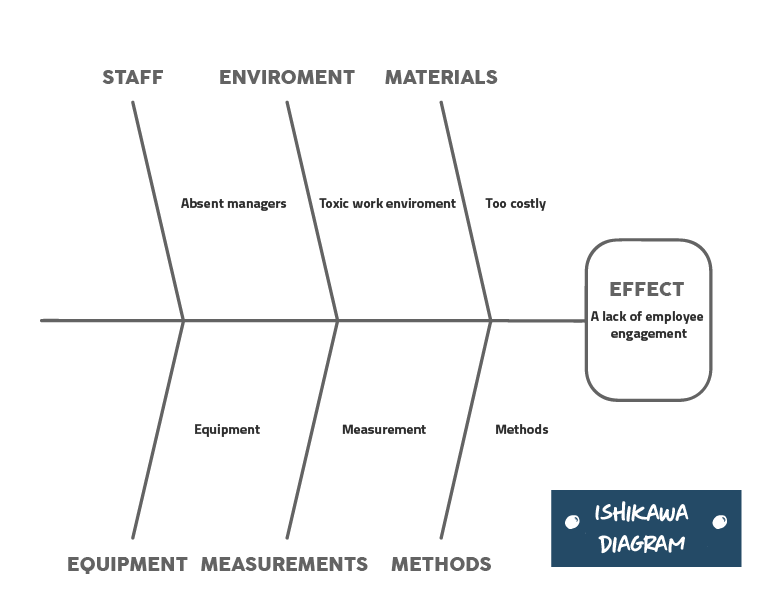
At this stage, the Ishikawa diagram, better known as Fishbone, can be used to help explain the causes and give visibility to the problem. For example, the problem analyzed is the lack of employee engagement of a company. The diagram can be done like this:
Step 2: Determination of Causes
It is in this phase that the possible causes that triggered the event appear in an organized and horizontal manner (everyone has the same opportunities to give their opinion). The facilitator should induce employees to reflect on these possible causes, exchange information about them and clarify doubts about their importance.
Following this example, post-its can be distributed to all participants, in which they can write down the possible causes that they think influence the problem. In this way, people’s participation becomes more horizontal and fair, as less interactive people can express themselves in the same way and the fear of judgment is also diminished.
Step 3: Hierarchization of Causes
After reading the possible causes for the problem, participants should determine their importance and reflect on them. In this step, you can use the 5 Whys method to delve deeper and find the root of the problems cited.
Using paper or post-its can also be helpful at this stage. If two or more people have written the same cause, it is important to consider it a priority. The facilitator will have this role of reading what was written and organizing it by relevance, subject etc. They have the role of classifying the pointed causes.
Step 4: Creating the Action Plan
Once you have defined the most and least important causes, it’s time to create countermeasures to get around the situation. It is important to ask which of these actions will have the most impact, which are the easiest, fastest, their financial cost, etc.
You can use the paper system again, in which they are handed over to participants who write what they believe is necessary to solve the problem.
If there is a wide range of actions, it may be a symptom that the causes have not yet been determined, so you need to go back to the previous step. If this does not happen, it is a sign that the Brainstorming is succeeding and that these countermeasures must also be ranked.
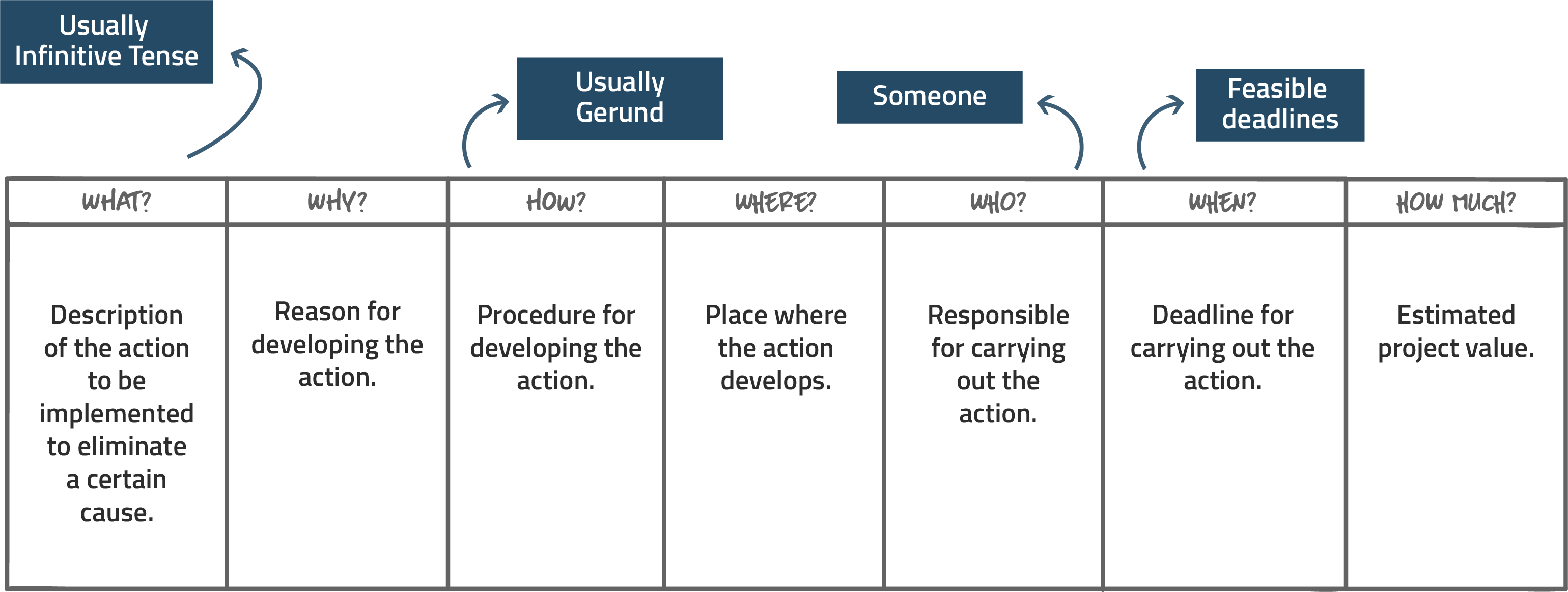
It is interesting to use the 5W2H methodology here, usually created in a table format (as shown below), which consists of asking some questions regarding the actions thought for a given problem, which are: what, why, where, who, when, how and how much.
What?
Increase employee engagement.
Why?
Performance has been falling and employee turnover is higher than desired.
How?
Enabling an organizational culture that welcomes employees and encourages their performance.
Where?
Throughout the organization.
Who?
CEOs, managers, etc.
When?
From the date of Brainstorming.
How much?
Define how much engagement actions cost the company.
We created a video with a summary of the steps for you to consult when you want, check below:
Conclusions
It is important to focus on each stage of Brainstorming, paying attention to the opinion of all participants and appreciating the facilitator’s good organization, so that the result of the process is enriching and positive.
In unsuccessful brainstorming, it is possible to notice that some mistakes were made during the development of the technique, which eventually result in dispersion of the team or limitation of the contribution of the involved ones.
Care must be taken that social dynamics are not dominated by individuals who intimidate others’ participation or fear of being judged by their own ideas. If this happens, there is no way to continue the brainstorming, it will be compromised.
It is important to create a comfortable and equitable environment for all participants for Brainstorming to be truly effective.
Did you enjoy learning about how to brainstorm step by step? Implement it in your company and tell us if it worked in the comments!
Revolutionize the management of your company with STRATWs One